all Computer Science classes are year-long & weighted tech electives
Why you should study Computer Science
The LASA{CS} course sequence covers the primary programming languages Python (Fundamentals), JAVA (AP), C++ (Advanced), and Javascript (Web & Mobile) as well as many data structures and algorithms. The Digital Electronics class covers transistors, logic, as well as low-level hardware & software concepts including the design & programming of a simple microprocessor.
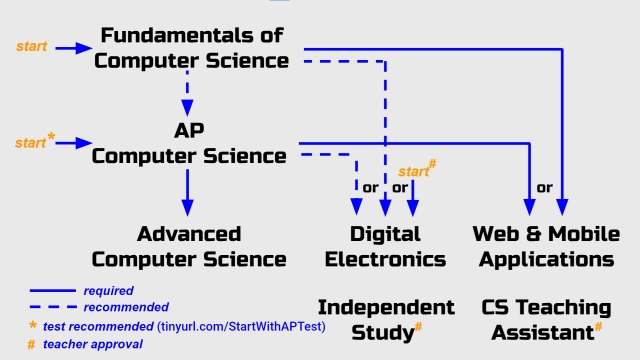
Should you start with Fundamentals of CS or AP CS?
If you want to take AP CS as your first CS class at LASA, we recommend you take this test (tinyurl.com/StartWithAPTest)
We strongly encourage students to start their LASA{CS} journey with the Fundamentals of Computer Science class. The primary goal of this course is to ensure that students have a solid foundation of fundamental Computer Science concepts using a variety of programming languages and environments. No prior experience is expected. This is your chance to really learn Python, a skill that will serve you well in just about any job you may end up in.
The AP Computer Science A class is for students that have either taken the LASA Fundamentals of Computer Science class or already have extensive procedural programming experience and are able to solve problems by writing basic algorithms and debugging their code. The primary focus of the AP class is learning object-oriented programming in JAVA.
In our experience, a rigorous middle school Computer Science class, in which a student develops their logic and debugging skills, prepares a student to succeed in AP CS as a freshman. However, very few Computer Science summer camps appear to have such rigor.
If you have any questions or are seeking teacher approval to take AP CS as a freshman, please contact Mr. Shockey ([email protected]) or Mr. Mueller ([email protected])
Course Descriptions
Fundamentals of Computer Science ( overview )
Grade Placement: 9–12 Credit: 1.0
Prerequisite: None
This course gives students a broad overview of computer science and an in depth exposure to procedural programming in Python. The course teaches students how to solve problems logically and efficiently, as well as to become a persistent debugger. The course does not require or expect any prior programming experience. Fundamental programming structures are introduced using Scratch and Jeroo. The course covers numeric, text, and image data representations; password security; Arduino coding; and Google App Scripts (docs/sheets/gmail) programming. By far the biggest unit is an in-depth study of procedural programming in Python – an easily accessible language hugely popular in industry and research due to its versatility. Students learn to write efficient loops, work with files, and effectively use data structures like lists, dictionaries, and tuples. This is the recommended entry point to the LASA Computer Science pathway. note1 note2 note3 note4 note5
AP Computer Science A ( overview )
Grade Placement: 9-12 Credit: 1.0
Prerequisite: Fundamentals of Computer Science or recommend student take test at tinyurl.com/StartWithAPTest
This course gives students a rigorous study of object oriented programming and various searching and sorting algorithms using JAVA exclusively. Students have the option of taking the AP test in May. Not recommended for students unless they have completed a rigorous programming course in Middle School and have developed basic debugging skills. AP CS can lead to 130 career areas and 48 college majors.
Digital Electronics ( overview ) PFLASA facebook post hackaday
Grade Placement: 10–12 Credit: 1.0
Prerequisite: Fundamentals of Computer Science or AP Computer Science or Teacher Approval
The goal of the class is to give students a foundational understanding of how computers work from the ground up. The class is a great basis for several engineering and/or CS college classes which will explore many of these concepts in more depth (and with more math). Starting with fundamental concepts of electricity, students will learn how transistors operate and can be used to construct everything from simple logic gates to complex processors. Students will explore resistive, capacitive, basic arduino, as well as many many logic circuits in hands-on projects and simulations. The major project is the design, simulation, and programming of a pipelined microprocessor. Students will often work in small groups, utilizing tools such as a multimeter, an arduino, an oscilloscope, the SPICE circuit simulator, the Logisim logic simulator, a logic analyzer, an ARM assembly language simulator, and a FPGA programming platform in their projects. note1 note2 note3 note4 note5 note6
Web and Mobile Applications ( overview )
Grade Placement: 10–12 Credit: 1.0
Prerequisite: Fundamentals of Computer Science or AP Computer Science
Moving beyond the static pages of the early web, today’s dynamic internet is based on serving web applications to users. Starting from the basics of how the web works, students will learn how to implement and deploy their own web applications. The projects will address password security as well as issues in scaling a web application to support large numbers of users. Topics covered include HTML, CSS, HTTP, JavaScript, cookies, processing user input, using databases, as well as security protocols and user verification. With mobile phone sales soon exceeding 2 billion units per year, mobile applications are in high demand. Develop real applications using Android Studio that run on your phone.
Advanced Computer Science ( overview )
Grade Placement: 10-12 Credit: 1.0
Prerequisite: AP Computer Science
Advanced CS provides a full Data Structures and Algorithms course as taught in most undergraduate programs. Along with touches of three other key topics; operating systems (with Linux examples), software engineering, and computer architecture and organization. The end of the course entails a practicum where students form teams to create an application of their choice and demonstrate mastery of techniques taught in the course. The teams use industry standard development tools and Agile project management methodology to implement the project. ACP teaches important topics that help students succeed at University and in industry.
Independent Study
Grade Placement: 11-12 Credit: 1.0
Prerequisite: Must be preceded by Advanced Computer Science and either Digital Electronics or Web & Mobile Applications. Requires teacher approval. Can be taken concurrently with Adv Computer Science, Digital Electronics, or Web & Mobile Applications.
If you have exhausted the entire Computer Science curriculum at LASA and you want to explore more about computer programming or hardware, then this course is the right fit for you. Students write a software or hardware project proposal and then work on projects. Students present their work to their peers.
Computer Science Teaching Assistant
Grade Placement: 11-12
Prerequisite: Teacher Approval
Why be an office aid if you can be a TA in the Fundamentals of Computer Science or the AP Computer Science class. Help students learn Computer Science, get a guaranteed req letter, bolster your resume, and still have plenty of time to work on your own projects or college apps. Get details from Mr. Mueller or Mr. Shockey.
Why CS WhyCS(short) seq Fundamentals OrAP Fundamentals AP DE WA lasacs.com announcements